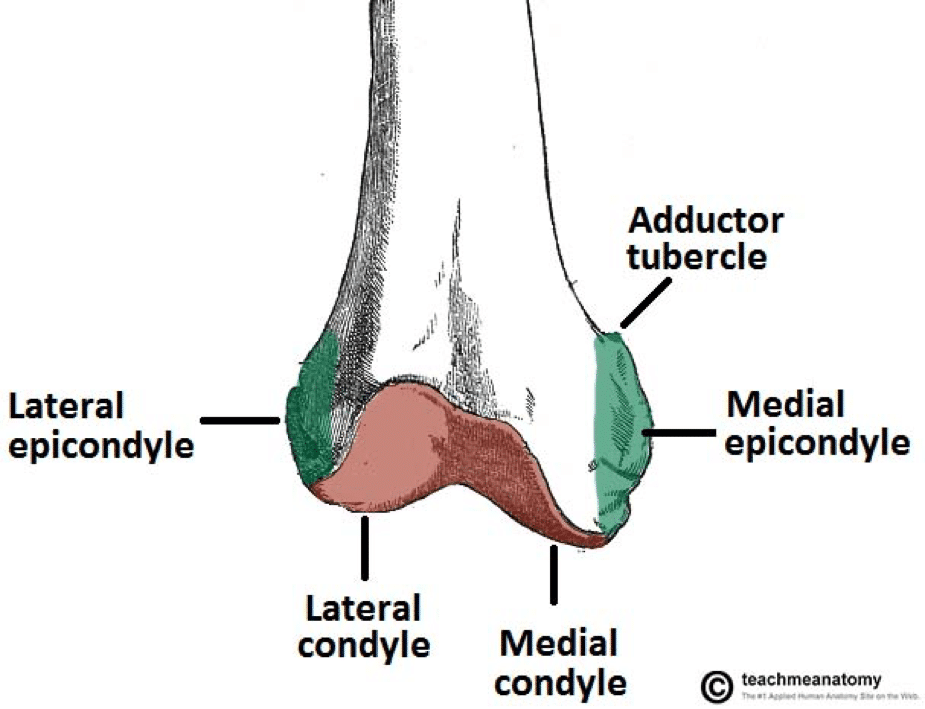
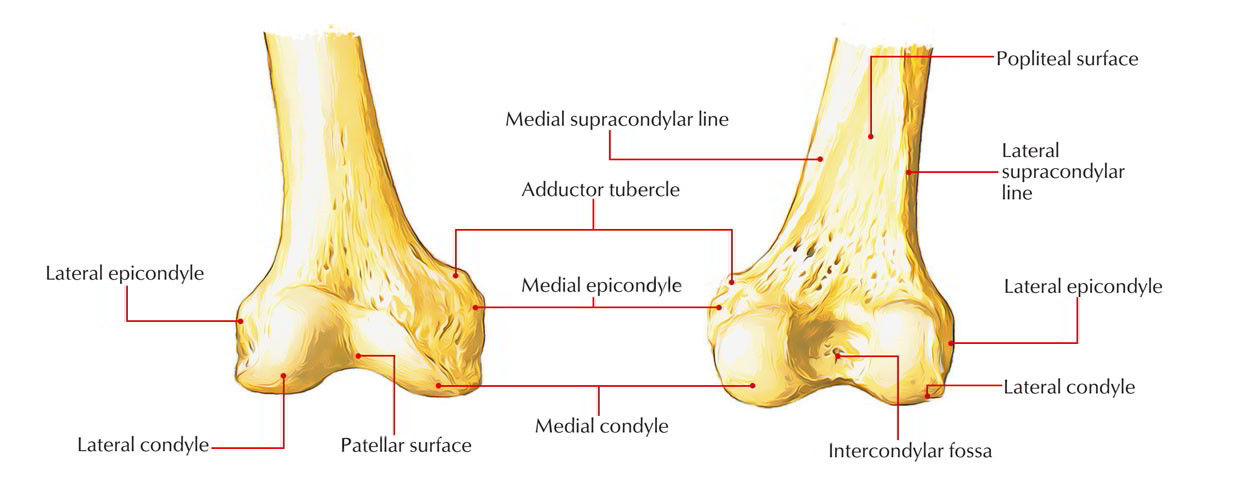
Learn more about the femur in this. They are the area of attachment of some muscles and the collateral ligaments of the knee joint.
Orif Lag Screw For Lateral Medial Femoral Epicondyle Fracture
They are separated by the deep intercondylar fossa proximally bounded by the horizontal intercondylar line.
. The motions of the condyles include rocking gliding and rotating. The medial femoral condyle MFC is wider and has a larger articulating surface area than the lateral condyle LFC although the LFC is larger anteroposteriorly. 4 rows In other words the lateral surface of the medial condyle the medial wall of the.
The medial condyle is one of the two projections on the lower extremity of femur the other being the lateral condyle. The medial femoral condyle is located on the inside part of the knee whereas the lateral femoral condyle which is bigger is. Learn How To Get Rid Of It.
Any abnormal surface structure or cartilage damage can lead to cartilage breakdown and arthritis loss of cartilage padding. The femoral condyles form the trochlear groove that provides the articulating surface of the femur. Name the bones that make up the hinge joint.
The articular cartilage thickness on the medial posterior femoral condyle was 3 mm 1 mm mean standard deviation and 1 mm 1 mm on the lateral side p-value. Palpable as a hard rounded bump to the inside of either knee joint they are one of two condyles at the bottom of each leg bone the other being the lateral femoral condyle. Medial Condyle Of Femur Lateral Condyle Of Femur Medial Collateral Ligament Posterior Cruciate Ligament The Knee.
Medial and lateral epicondyles Bony elevations on the non-articular areas of the condyles. A femoral condyle is the ball-shape located at the end of the femur thigh bone. The lateral condyle is the more prominent and is broader both in its front-to-back and transverse diameters.
There are two femoral condyles. The most accurate equation used width of the medial and lateral condyles WDC with of the medial condyle WMC depth of the lateral condyle DLC and depth of the intercondylar notch DIN 941 and is as follows. At the end of the medial supracondylar line is a tubercle called the adductor tubercle.
Mean medial condyle BMDs medial versus lateral condyle BMD ratios and visual analog scale VAS pain in both the femur and the tibia were higher in the obliteration group compared with the narrowing group P 0001 for all. The paired femoral condyles are situated to either side of the patella or kneecap. The lateral condyleis one of the two projections on the lower extremity of the femur.
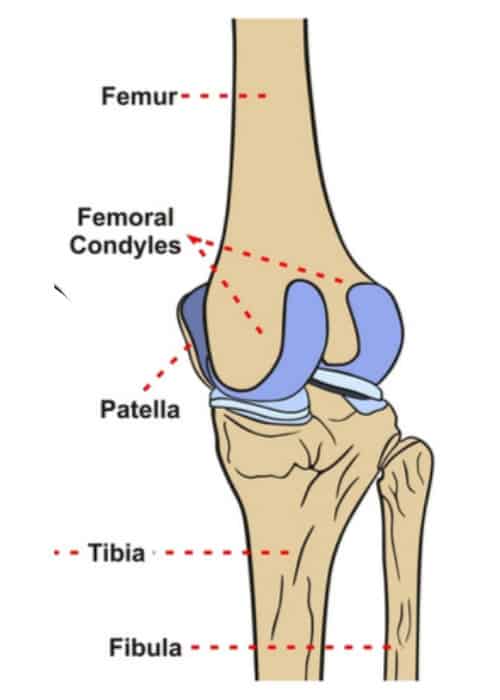
Tibia -- Femur Gliding. TERMS IN THIS SET 31 Movements Allowed by Knee. The femoral condyles are the two rounded prominences at the end of the femur.
Ad Learn About Lateral Meniscus Injuries Then Learn How to Treat It Effectively. The medial and lateral condyles form the proximal part of the body of femur and articulate with the proximal part of tibia to form the femorotibial joint. They are called the medial and the lateral femoral condyle respectively.
The lateral condyle is called the capitulum and the medial condyle is called the trochlea. The medial femoral condyles are the bony protrusions on the inside edge of the bottom of the femur bone in each thigh. The medial condyle is larger than the lateral outer condyle due to more weight bearing caused by the centre of mass being medial to the knee.
A significant positive correlation was observed between the femoral and tibial condyles in the following parameters. A Torn Lateral Meniscus Will Seriously Impact Your Life. The medial condyle is one of the two projections on the lower extremity of femur the other being the lateral condyle.
The lateral condyle is the more prominent and is the broader both in its antero-posterior and transverse diameters the medial condyle is the longer and when the femur is. The medial condyle is larger than the lateral outer condyle due to more weight bearing caused by the centre of mass being medial to the knee. The mean lateral femoral condyle ratios and standard deviations were 612 24 in the control group 642 38 in the primary ACL injury group 644.
Which femoral condyle is wider transversely. Leg flexion extension and limited rotation. The distal end of the humerus forms two condyles.
In between the medial and lateral femoral condyles is the intercondylar fossa. The medial condyle is larger than the lateral outer condyle due to more weight bearing caused by the centre of mass being medial to the knee. On each condyle is a smaller epicondyle which serve as the point of attachment for the collateral ligaments the medial collateral MCL and the lateral collateral ligaments LCL.
Intercondylar fossa A depression found on the posterior surface of the femur it lies in between the two condyles. If there is a fracture break in part of the condyle this is known as a fracture of the femoral condyle. Anatomical terms of bone.
While both bones feature a medial and lateral condyle with the lateral condyle on the other side of the knee the medial condyle is the larger prominence because more weight is transferred across the inside aspect of the knee joint. The medial condyle is one of the two projections on the lower extremity of femur the other being the lateral condyle. D 0336 WDC -0097 WMC -0153 DLC 0372 DIN - 20912.
They are the pair of rounded eminences that form the. There are two condyles on each leg known as the medial and lateral femoral condyles. The posterior and inferior surfaces articulate with the tibia and menisci of the knee while the anterior surface articulates with the patella.
Similar to the articular surface of the patella the trochlear surface is divided into medial and lateral facets the lateral facet being larger and extending more proximally and anteriorly than its medial counterpart Figure 22-2. The other one is the medial condyle. The medial condyle is larger than the lateral outer condyle due to more weight bearing caused by the centre of mass being medial to the knee.
There is a significant difference in articular cartilage thickness between the medial and lateral posterior femoral condyles in patients undergoing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. Contents Clinical significance Additional images References External links Clinical significance. Medial and lateral condyles rounded areas at the end of the femur.
The anterior articular surfaces of the condyles become less convex and form a V-shaped groove known as the trochlear sulcus that articulates with the patella. On the posterior surface of the condyle the linea aspera a ridge with two lips. In terms of aligning the femoral component the most important kine- matic axis of the knee passes through the center point of the best-fit circles of the medial and lateral femoral condyles and is termed the primary femoral axis about which the tibia flexes and extends3-7.

Medial Condyle Of Femur Wikipedia

Femur An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Distal Femur Fracture Teachmesurgery
Femoral Condyle Articular Cartilage Injury Minneapolis St Paul Edina Eagan Mn


0 comments
Post a Comment